Debug
This tab allows you to manage debug settings.
Warning: Use very carefully! Turning these options on can produce (and probably will) huge amount of logs.
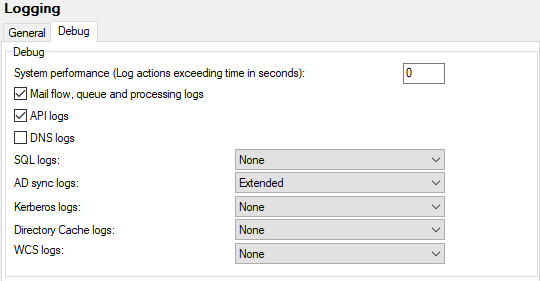
Figure. Logging management: Debug tab.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
System performance (Log actions exceeding time in seconds) |
Insert time in seconds, if you want to have logged system actions lasting longer than the value specified here. |
|
Check the box if you want to have logged most actions performed with email messages (antispam, antivirus, etc.) This feature logs actions taken after an email is received via SMTP and can indicate bottle necks, such as heavy content filters (that scan body of messages without a message size limitation). For very experienced administrators. Note: The kind of logs where content filters / rules are mentioned differ: When a CF / rule alters mail delivery, it is written in SMTP logs (e.g.: rejection). When it alters spam/nospam behavior, it is in AntiSpam logs (e.g.: rejection, change spam score, etc.). |
|
|
API logs |
Check the box if you want to have logged every API use. This includes not only any server setting change, but also for example any setting changes performed by users in their WebClients etc. |
|
DNS logs |
Check the box if you want to have logged DNS service and communication with your DNS server. |
|
SQL logs |
Select how you want to have logged database actions:
|
|
AD sync logs |
Select how you want to have logged Active Directory synchronization:
|
|
Kerberos logs |
Select how you want to have logged Kerberos authentication. Only the Debug and Extended levels produce outputs. For more details, refer to the Domains and Accounts: Domain: Directory Service chapter: Kerberos/GSSAPI/SSO section. |
|
Directory Cache logs |
Select how you want to have logged directory cache:
For more details on directory cache, refer to Directory Cache. |
|
WCS logs |
Select how you want to have logged WCS (Web Coverage Service):
|

