What is Desktop Office
Desktop Office is a powerful kit of office software, that includes:
Desktop Office is a part of a bigger package, Desktop Suite, that includes also IceWarp Desktop Client.
To install Desktop Office, go to the IceWarp download portal.
Converting a VBA Macro to a JavaScript Macro
This tutorial shows how to recreate a simple Microsoft Office VBA macro as a macro written in JavaScript.
1. Overview
Original VBA Macro Example
vba
Sub Button1_Click()
Dim cell As Range
' Scan constant values in D1:D10
For Each cell In Range("D1:D10").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants, 23)
' If the value matches TODAY(), write [This_value] to the cell on the right
If cell.Value = [TODAY()] Then
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = [This_value]
End If
Next cell
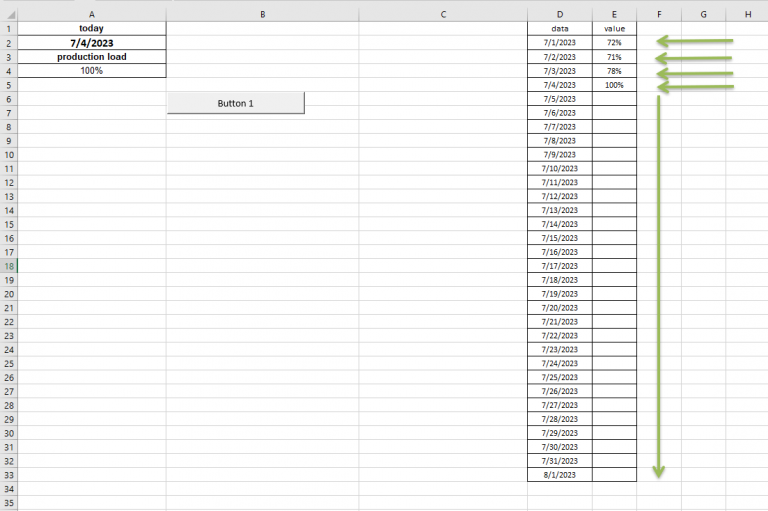
End SubScreenshot of the example spreadsheet used in the macro.
What This Macro Does
- Scans column D for constant values.
- Compares each value with the value in
TODAY(). - If they match, writes a value into column E.
Assumptions for This Example
TODAY()value is stored in cell A2.[This_value]is stored in cell A4.
2. Preparing the Spreadsheet
Open the spreadsheet.
Required Cell Setup
- Cell A2 contains the date or value used for comparison.
- Cell A4 contains the value that will be written to column E.
- Column D contains the values to check (for example, range
D1:D10).
You can adjust these cells and ranges later to match your own data.
3. Building the macro in JavaScript
Macros use JavaScript and the Spreadsheet API. The goal is to reproduce the same behavior as the VBA macro: scan column D, compare each value with the value in cell A2, and write the value from A4 into column E when they match.
Required API Methods
These API methods will be used in the JavaScript macro.
Api.GetActiveSheet()– gets the active sheet.sheet.GetRange("A1")– selects a cell or range.range.GetValue()andrange.SetValue()– used to read and write cell values.range.ForEach()– loops through all cells in a range.
JavaScript Version of the Macro
js
(function () {
// Get the active sheet
var sheet = Api.GetActiveSheet();
// Read the comparison value (equivalent to TODAY()) and the value to write
var dateValue = sheet.GetRange("A2").GetValue();
var writeValue = sheet.GetRange("A4").GetValue();
// Range in column D to check
var dataRange = sheet.GetRange("D1:D10");
// Loop through each cell in the range
dataRange.ForEach(function (cell) {
var currentValue = cell.GetValue();
// If the value matches, write to the corresponding cell in column E
if (currentValue === dateValue) {
var row = cell.GetRow(); // row number of the current cell
var target = sheet.GetRange("E" + row); // matching row in column E
target.SetValue(writeValue);
}
});
})();This macro reproduces the behavior of the original VBA code
Video tutorial:
Click here to open the macro demo video
4. Running and Adapting the Macro
- Open Plugins → Macros in the Spreadsheet Editor.
- Create a new macro and paste the JavaScript code above.
- Run the macro and verify that:
- Cells in column E are updated only for rows where the value in column D matches the value in A2.
To adapt it to your own scenario:
- Change
"A2"and"A4"if your reference cells are different. - Adjust
"D1:D10"to cover the full range you need (for example"D1:D1000"). - Modify the condition inside the loop if you need a different comparison (e.g.,
currentValue === dateValue, greater than, less than, not equal, etc.).
5. General Tips for Converting Other VBA Macros
When converting more complex macros, the same approach applies.
Understand the VBA logic first
Which sheet is used?
Which ranges are read or written?
What are the conditions and loops?
Map VBA features
Range / Cells →
GetRange().Value→GetValue()/SetValue()For Each→ForEach()Offset(row, col)→ construct a new address using row and column information (for example, usingGetRow()together with a fixed column letter such as"E").
Rewrite in JavaScript using the same logical steps.
Test and refine until the behavior matches your original macro.